Search engines have become an inseparable part of our daily lives. Whether we’re looking for a nearby restaurant, learning a new skill, or researching a product before buying — we rely on Google, Bing, and other search engines to give us the right answers in seconds.
But have you ever wondered how search engines actually work ? How do they find millions of web pages, analyze them, and show you the best results almost instantly?
In this blog, we’ll break it down step by step so you can understand how search engines work — and how you can use that knowledge to improve your website’s SEO.
What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a software system designed to search the internet and provide relevant results based on a user’s query. The most popular search engine is Google, which holds over 90% of the global market share, followed by Bing, Yahoo, Yandex, and Baidu.
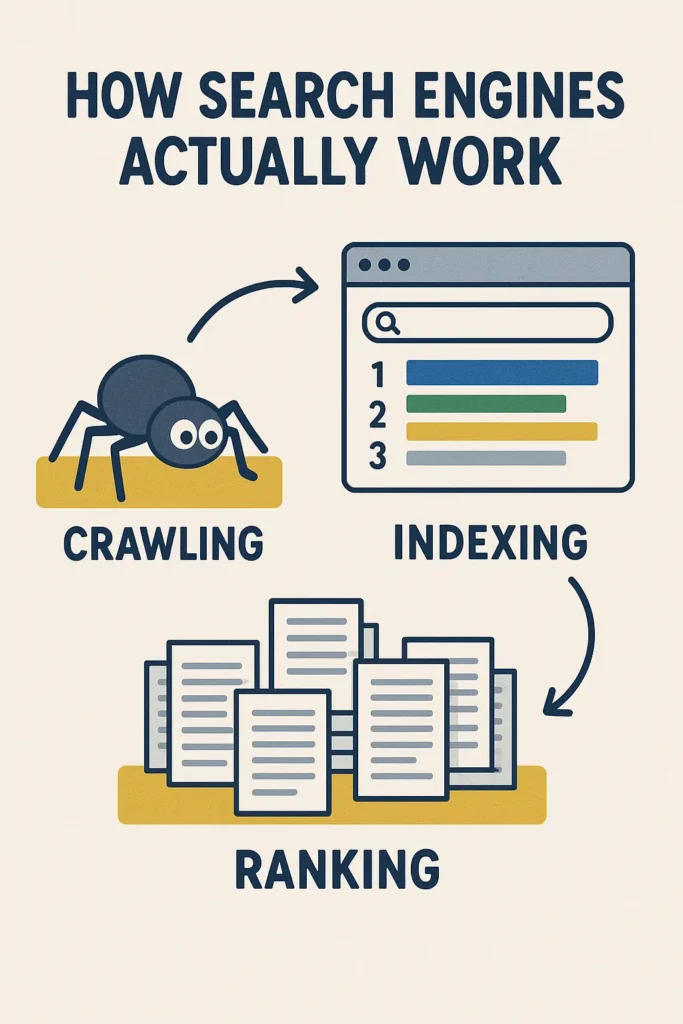
At its core, a how search engines actually work performs three major functions:
- Crawling – Finding and discovering web pages across the internet.
- Indexing – Storing and organizing the discovered content.
- Ranking – Displaying the most relevant pages for a user’s query.
Let’s dive deeper into each stage.
Step 1: Crawling – Discovering Web Pages
Crawling is the first step of how search engines work.
Search engines use special programs called crawlers or spiders (Google’s crawler is called Googlebot) that browse the internet. They start with a list of known websites and follow links from one page to another, discovering new content as they go.
How Search Engines Actually Work: Crawling Explained
- Crawlers request a website’s pages just like a browser does.
- They check the website’s robots.txt file to see which pages are allowed to be crawled.
- They follow internal links (within the site) and external links (to other websites).
- They keep coming back to websites periodically to find new or updated content.
Best Practices to Help Crawlers
- Make sure your website is crawlable (no accidental blocking in robots.txt).
- Use a sitemap.xml file to tell search engines about your pages.
- Fix broken links (404 errors) that may stop crawlers from discovering your content.
Step 2: How Search Engines Actually Work: Indexing Your Content
After crawling, search engines store the information in a massive database called the index. Think of the index as a library where every page is cataloged for quick retrieval.
During indexing, search engines analyze:
- Page Content – The text, keywords, and overall topic.
- Meta Tags – Title tags and meta descriptions.
- Images & Alt Text – To understand visual content.
- Internal Links – How pages are connected within your site.
- Structured Data – Schema markup that helps search engines understand context (e.g., FAQ schema, product schema).
Why Indexing Matters
If your page isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results — no matter how good it is.
How to Check Indexing
- Use site:yourwebsite.com/page-url on Google to see if it’s indexed.
- Use Google Search Console → Coverage Report to find indexed pages and errors.
Step 3: Ranking – Showing the Best Results
Once a page is crawled and indexed, the search engine decides where it should appear in search results. This is called ranking.
Ranking is determined by hundreds of factors, often referred to as Google’s ranking algorithm. Some of the most important ranking factors include:
- Relevance – How closely the page matches the search query.
- Quality of Content – Expertise, depth, and originality.
- User Experience – Mobile-friendliness, page speed, and layout.
- Backlinks – The number and quality of external websites linking to the page.
- Search Intent – Whether the page satisfies what the user is looking for (informational, transactional, etc.).
Example of Ranking in Action
When you search “best running shoes for men,” Google:
- Understands that you’re looking for product recommendations (commercial intent).
- Finds pages that review or list running shoes.
- Ranks them based on relevance, quality, authority, and user engagement.

Search Engine Algorithms
Search engines use complex algorithms to evaluate and rank content. Google frequently updates its algorithm to improve search results quality.
Some well-known updates include:
- Panda Update – Focused on content quality.
- Penguin Update – Penalized spammy backlinks.
- Hummingbird Update – Improved understanding of search intent.
- RankBrain – Uses machine learning to refine results.
- Helpful Content Update – Prioritizes people-first content over keyword-stuffed articles.
Staying updated on these changes helps you avoid ranking drops and stay competitive.
Additional Factors: Personalization & Localization
how search engines actually work also personalize results based on:
- Location: Someone searching “pizza near me” will see nearby restaurants.
- Search History: Google tailors results based on past searches.
- Device Type: Mobile users might see different results than desktop users.
This is why SEO is not one-size-fits-all — local businesses must focus on local SEO to rank for location-based queries.
Why Understanding Search Engines Matters for SEO
If you know how search engines work, you can:
- Make sure your website is crawlable and indexable.
- Create content that matches search intent.
- Build high-quality backlinks to improve authority.
- Optimize your website’s technical SEO to improve rankings.
Simply put, understanding search engines is the first step to mastering SEO.
Pro Tips for Better Visibility
- Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console.
- Regularly update old content to stay relevant.
- Use structured data (schema) to enhance search appearance.
- Improve page speed and mobile responsiveness.
- Focus on E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
Conclusion
Search engines are sophisticated systems that crawl, index, and rank billions of pages every day — all to give users the best possible answers. By understanding how they work, you can optimize your website strategically, improve rankings, and attract more targeted traffic.
The key takeaway: focus on quality content, technical SEO, and user experience. This combination will help search engines trust your site and reward you with higher visibility.
Frequently Asked Questions.
Q1: How long does it take for a new page to get indexed?
Usually, it takes anywhere from a few hours to a few days. Submitting your sitemap and using Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool can speed up indexing.
Q2: Can I make my site un-crawlable?
Yes. You can block crawlers using robots.txt or noindex tags. But be careful — blocking important pages can hurt SEO.
Q3: Do all search engines work the same way?
Most follow the same basic process (crawl → index → rank), but algorithms and ranking signals may vary slightly.
Q4: How often do search engines crawl a website?
It depends on your website’s size, popularity, and update frequency. High-authority sites are crawled more often.
Q5: Why do some pages not show up in search results?
They may not be indexed yet, blocked by robots.txt, penalized, or have duplicate content issues.
Q6: Does paying for ads improve organic ranking?
No. Paid ads (Google Ads) don’t affect organic rankings, but they can boost visibility temporarily.